68603-87-2
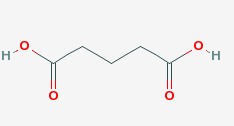
- Product Name:Oxalic Acid
- Molecular Formula:C5H8O4
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:132.11
Product Details;
CasNo: 68603-87-2
Molecular Formula: C5H8O4
Factory Supply 68603-87-2 with Safe Delivery, Export Oxalic Acid
- Molecular Formula:C5H8O4
- Molecular Weight:132.11
- Vapor Pressure:<0.01 mm Hg ( 20 °C)
- Melting Point:189.5ºC (dec.)(lit.)
- Boiling Point:302.894 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:4.43[at 20 ℃]
- Flash Point:151.212 °C
- PSA:223.80000
- Density:1.317 g/cm3
- LogP:0.97770
- IDLH: 500 mg/m3See: 144627
OXALIC ACID(Cas 68603-87-2) Usage
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Notclassified |
| Description | Oxalic acid, also known as ethanedioic acid or oxiric acid, is a colorless, crystalline organic compound with toxic properties. It exists as a white crystalline solid that forms a colorless solution in water. This compound is naturally present in various vegetables and plants, including spinach, cabbage, broccoli, parsley, and tomatoes. |
|
EXPOSURE ROUTES |
inhalation, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact |
|
FIRST AID |
(See procedures) Eye:Irrigate immediately Skin:Water flush promptly Breathing:Respiratory support Swallow:Medical attention immediately |
InChI:InChI=1/C5H8O4/c6-4(7)2-1-3-5(8)9/h1-3H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)
68603-87-2 Relevant articles
Theoretical Study of Thermal Decomposition Mechanism of Oxalic Acid
James Higgins, Xuefeng Zhou, Ruifeng Liu, and Thomas T.-S. Huang
, J. Phys. Chem. A 1997, 101, 14, 2702–2708
The B3LYP structures and relative energies of the rotational isomers of oxalic acid are found very similar to MP2 results, confirming that the most stable isomer is the doubly intramolecular hydrogen-bonded C2h structure E1, with four other planar isomers within 6 kcal/mol.
Oxalic Acid in Foods and its Behavior and Fate in the Diet: Three Figures
EF Kohman
, The Journal of Nutrition, 1939
By direct titration of a highly diluted sample, after filtration if necessary, the chlorine in the two fractions was determined. On the assumption that the oxalic acid distributed itself in the same ratio as the chlorine, it could be calculated for the entire sample by a determination on the drained fraction.
Relevant Products
-
Azithromycin dihydrate
CAS:117772-70-0
-
Cellulose acetate
CAS:9004-35-7
-
Ammonium L-tartrate
CAS:3164-29-2