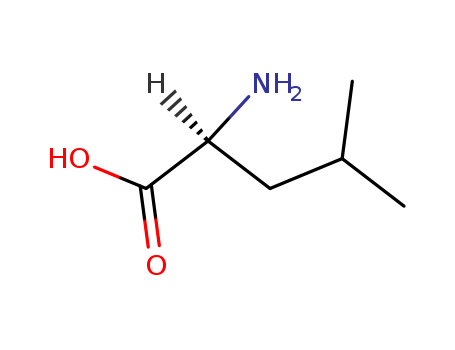
61-90-5
- Product Name:L-Leucine
- Molecular Formula:C6H13NO2
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:131.175
Product Details;
CasNo: 61-90-5
Molecular Formula: C6H13NO2
Appearance: White crystalline powder
Buy Quality High Purity 61-90-5 In Bulk Supply
- Molecular Formula:C6H13NO2
- Molecular Weight:131.175
- Appearance/Colour:White crystalline powder
- Vapor Pressure:<1 hPa (20 °C)
- Melting Point:>300 °C(lit.)
- Refractive Index:1.4630 (estimate)
- Boiling Point:225.8 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:2.328(at 25℃)
- Flash Point:90.3 °C
- PSA:63.32000
- Density:1.036 g/cm3
- LogP:1.14470
- IDLH:1423
- IDLH:10482
- IDLH:3297
L-Leucine(Cas 61-90-5) Usage
|
description |
L-Leucine is an essential amino acid, one of the twenty types that constitute proteins, and it belongs to the aliphatic amino acid group. It forms part of the trio known as branched-chain amino acids, along with L-isoleucine and L-valine. As a white hexahedral crystal or crystalline powder, it is odorless and slightly bitter. L-Leucine exhibits stability in aqueous mineral acids in the presence of hydrocarbons. |
|
Chemical Properties |
White shiny hexahedral crystals or white crystalline powder. Slightly bitter (DL-leucine is sweet). Sublimation at 145~148 ℃. Melting point 293~295 ℃ (decomposition). It belongs to the essential amino acids,and adult men requirement is 2.2g/d (151 version). It is necessary in normal growth for infants and maintaining normal nitrogen balance for adults. Natural products are found in the spleen, heart, etc., and are present in a variety of plant and animal tissues in the form of the proteins, free out after decomposition and corruption. |
|
Uses |
L-Leucine is commonly used in amino acid infusions and comprehensive amino acid preparations for medical treatment or healthcare. It finds applications in food, cosmetics, and feed additives, serving as a plant growth promoter. Natural sources of leucine include brown rice, beans, meat, nuts, soy flour, and whole wheat. However, excessive intake can lead to side effects such as pellagra, vitamin A deficiency, dermatitis, diarrhea, and mental disorders. Diets rich in leucine may increase ammonia levels in the body, potentially harming liver and kidney functions. Therefore, caution is advised, especially for individuals with impaired liver or kidney function. The synthesis of L-Leucine can occur through various methods, including bromination followed by amination of isocaproic acid, acetamidomalonic ester, and isolation from gluten, casein, and keratin. As a non-glucogenic essential amino acid, L-Leucine is a structural component of proteins, positively influencing insulin release and contributing to the elimination of toxic sugars from the bloodstream. Its degradation results in the formation of ketone bodies. |
|
toxicity |
Safe for food (FDA, §172.3202000). LD505379mg/kg (rat, subcutaneously). |
|
Occurrence |
Reported found as a constituent in proteins; also present in the free state in the human body |
|
Production Methods |
Leucine is produced microbially by incubating an amino-acidproducing microorganism including but not exclusive to Pseudomonas, Escherichia, Bacillus, or Staphylococcus in the presence of oxygen and a hydrocarbon. The nutrient medium should contain an inhibitory amount of a growth inhibitor that is a chemically similar derivative of leucine (e.g. methylallylglycine, a-hydrozinoisocaproic acid, or b-cyclopentanealanine) to inhibit the growth of the organism except for at least one mutant that is resistant to the inhibitory effect. The resistant mutant is then isolated and grown in the presence of oxygen and the hydrocarbon in the absence of the inhibitor. The mutant cells are then harvested and a nutrient medium is formed that includes a hydrocarbon as the sole source of carbon. Finally, the harvested cells are incubated in the medium in the presence of oxygen. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: The L-enantiomer of leucine. |
|
Preparation |
By bromination followed by amination of isocaproic acid; via the acetamidomalonic ester; by isolation from gluten, casein, keratin; from hydantoin. |
|
Pharmaceutical Applications |
Leucine is used in pharmaceutical formulations as a flavoring agent. It has been used experimentally as an antiadherent to improve the deagglomeration of disodium cromoglycate micro-particles and other compounds in inhalation preparations; and as a tablet lubricant. Leucine copolymers have been shown to successfully produce stable drug nanocrystals in water. |
|
Safety |
Leucine is an essential amino acid and is consumed as part of a normal diet. It is generally regarded as a nontoxic and nonirritant material. It is moderately toxic by the subcutaneous route. LD50 (rat, IP): 5.379 g/kg |
|
storage |
Leucine is sensitive to light and moisture, and should be stored in an airtight container in a cool, dark, dry place. |
|
Incompatibilities |
Leucine is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
|
Regulatory Status |
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IV infusion; oral tablets). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. |
|
Who Evaluation |
Evaluation year: 2004 |
|
Consumer Uses |
ECHA has no public registered data indicating whether or in which chemical products the substance might be used. ECHA has no public registered data on the routes by which this substance is most likely to be released to the environment. |
InChI:InChI=1/C6H13NO2/c1-4(2)3-5(7)6(8)9/h4-5H,3,7H2,1-2H3,(H,8,9)/t5-/m0/s1
61-90-5 Relevant articles
Structures and antitumor activities of ten new and twenty known surfactins from the deep-sea bacterium Limimaricola sp. SCSIO 53532
Chen, Min,Chen, Rouwen,Ding, Wenping,Li, Yanqun,Tian, Xinpeng,Yin, Hao,Zhang, Si
, (2022/01/11)
Surfactins are natural biosurfactants wi...
Recreating the natural evolutionary trend in key microdomains provides an effective strategy for engineering of a thermomicrobial N-demethylase
Gu, Zhenghua,Guo, Zitao,Shao, Jun,Shen, Chen,Shi, Yi,Tang, Mengwei,Xin, Yu,Zhang, Liang
, (2022/03/09)
N-demethylases have been reported to rem...
Leveraging Peptaibol Biosynthetic Promiscuity for Next-Generation Antiplasmodial Therapeutics
Lee, Jin Woo,Collins, Jennifer E.,Wendt, Karen L.,Chakrabarti, Debopam,Cichewicz, Robert H.
supporting information, p. 503 - 517 (2021/03/01)
Malaria remains a worldwide threat, affl...
Potential antiproteolytic effects of L-leucine: observations of in vitro and in vivo studies
Nelo E Zanchi, Humberto Nicastro & Antonio H Lancha Jr
, Nutrition & Metabolism volume 5, Article number: 20 (2008)
The purpose of present review is to describe the effect of leucine supplementation on skeletal muscle proteolysis suppression in both in vivo and in vitro studies. Most studies, using in vitro methodology, incubated skeletal muscles with leucine with different doses and the results suggests that there is a dose-dependent effect.
61-90-5 Process route
-
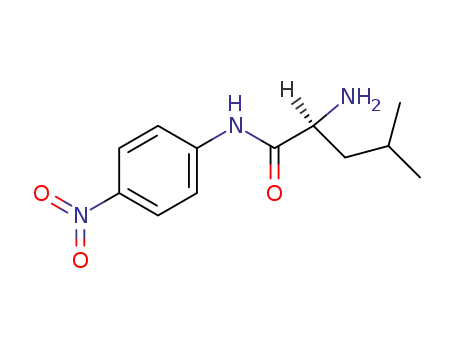
- 4178-93-2,110893-28-2,86237-92-5,63324-49-2,6664-98-8
(S)-2-amino-4-methyl-N-(4-nitrophenyl)valeramide

-
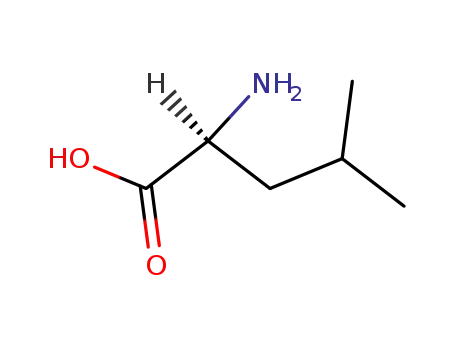
- 61-90-5,21675-61-6,25248-98-0,70-45-1
L-leucine
-
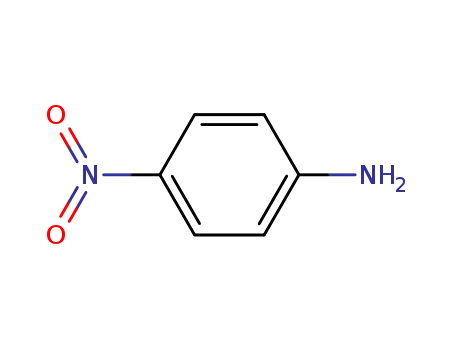
- 100-01-6,104810-17-5
4-nitro-aniline
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With water; leucine aminopeptidase; at 25 ℃; under 750.06 Torr; Rate constant; Thermodynamic data; influence of Zn(2+), influence of pH, Mg(2+) modified enzyme, different pressures, activation volume;
|
|
|
With Streptomyces griseus dizinc aminopeptidase; water; calcium(II) ion; In various solvent(s); at 30 ℃; pH=8.0; Enzyme kinetics;
|
|
|
With Tris-HCl buffer; an aminopeptidase from the seeds of Cannabis sativa; water; at 37 ℃; pH=7.5; Enzyme kinetics; Enzymatic reaction;
|
|
|
With aminopeptidase N; at 37 ℃; for 0.25h; pH=8.0; Enzyme kinetics;
|
|
|
With Zn(II) complex with a macrocycle ligand; tetramethylammonium nitrate; In various solvent(s); at 34.95 ℃; Further Variations:; Reaction partners; pH-values; Product distribution;
|
|
|
With MacIlvaine buffer; Patinopecten yessoensis mid-gut gland aminopeptidase; at 30 ℃; pH=7.0; Enzyme kinetics;
|
-
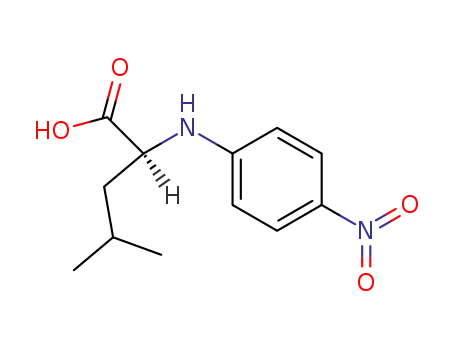
- 129297-64-9
L-Leucine p-nitroanilide

-

- 61-90-5,21675-61-6,25248-98-0,70-45-1
L-leucine

-

- 100-01-6,104810-17-5
4-nitro-aniline
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
at 24 ℃; Rate constant; pH 7.96, MgCl2, phosphate, Tris; effect of an RRF on AP-cytosol activity;
|
61-90-5 Upstream products
-
16979-05-8
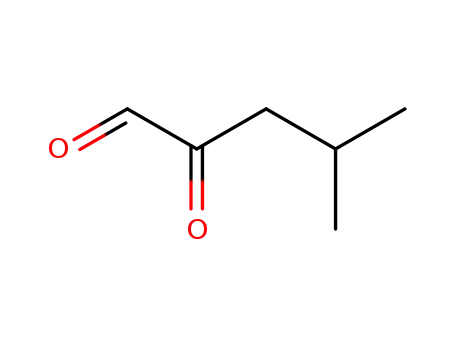
isobutyl glyoxal
-
13079-20-4
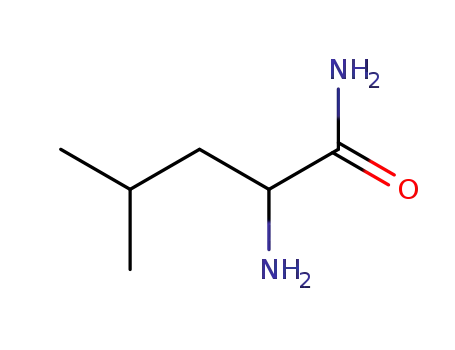
2-Amino-4-methyl-pentanoic acid amide
-
328-39-2

LEUCINE
-
2666-93-5
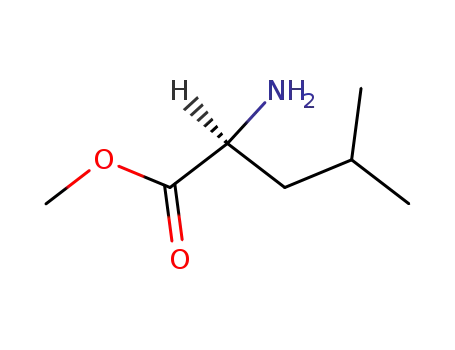
(S)-Leu-OMe
61-90-5 Downstream products
-
2666-93-5

(S)-Leu-OMe
-
118660-40-5
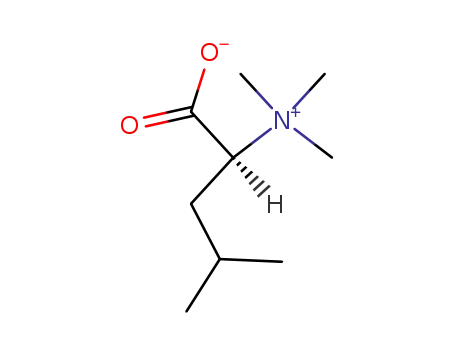
leucine betaine
-
99-15-0
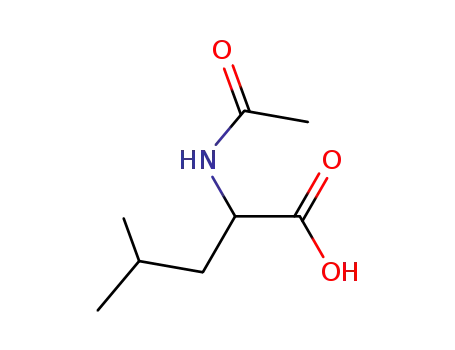
N-acetylleucine
-
1188-21-2
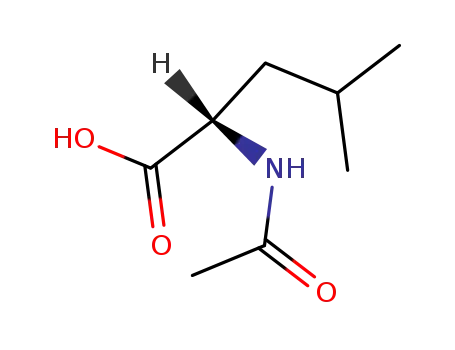
N-Ac-Leu
Relevant Products
-
Azithromycin dihydrate
CAS:117772-70-0
-
HYDROGEN TETRACHLOROAURATE(III)
CAS:16961-25-4