7789-41-5
- Product Name:Calcium bromide
- Molecular Formula:CaBr2
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:199.886
Product Details;
CasNo: 7789-41-5
Molecular Formula: CaBr2
Appearance: white powder
Buy Reliable Quality Top Purity Calcium bromide 7789-41-5 Competitive Price
- Molecular Formula:CaBr2
- Molecular Weight:199.886
- Appearance/Colour:white powder
- Vapor Pressure:0Pa at 25℃
- Melting Point:730 °C
- Boiling Point:806-812°C
- Flash Point:806-812°C
- PSA:0.00000
- Density:3.353 g/cm3
- LogP:-5.99200
Calcium bromide(Cas 7789-41-5) Usage
|
Uses |
Calcium bromide has a molecular weight of 199.90 g/mol for the anhydride and a specific gravity of 3.41 g/cm3. In its solid anhydrous state, it is a white powder with a melting point of 730°C and a boiling point of 810°C, where it decomposes. When heated in air, it produces lime (CaO) and bromine (Br2). The compound is commonly found as the dihydrate (CaBr2·2H2O), which appears as a white crystalline powder. There is also a hexahydrate form (CaBr2·6H2O). |
|
Description |
Calcium bromide (CaBr2) is a versatile chemical compound with various applications. Primarily known for its use as a developer in photographic film and paper, it also serves as a dehydrating agent, food preservative, and fire retardant. First prepared in 1924, it exists as a deliquescent salt, forming colorless hexagonal crystals that are soluble in water and absolute alcohol. The anhydrous form, obtained through dehydration, is a white powder. |
|
Chemical Properties |
Calciumbromide, CaBr2, is a colorless crystalline solid with a melting point of 765°C. It is deliquescent and is soluble in water and absolute alcohol. Calcium bromide is used in medicine. Calcium bromide(hydrated), CaBr2·3H20, has a meiting point of 80.5℃. |
|
Preparation |
CaBr2·2H2O has a melting point of 38°C where it dissolves in its own waters of hydration. Its density is 2.290 g/cm3. It can be prepared by reaction in solution with HBr on the carbonate: CaCO3 (solid)+HBr (liq)→CaBr2 (liq)+ CO2 (gas) An improved method for producing calcium bromide has been developed by reacting hydrogen bromide with calcium hydroxide in the presence of water. |
InChI:InChI=1/2BrH.Ca/h2*1H;/q;;+2/p-2
7789-41-5 Relevant articles
The melting point adjustment of calcium chloride hexahydrate by addition of potassium chloride or calcium bromide hexahydrate
H Feilchenfeld, J Fuchs, F Kahana, S Sarig
, Sol. Energy;(United Kingdom), 1985
This can be achieved by addition of a second salt. This second salt may or may not form solid solutions with the main component. In this paper we deal with an example for each case. CCH forms solid solutions with calcium bromide hexahydrate, but not with potassium chloride. The influence of these two salts on the melting behavior of CCH is discussed.
Differential thermal analysis under quasi-isothermal, quasi-isobaric conditions (Q-DTA) Part II. Water evaporation and the decomposition mechanism of compounds with structural and crystal water
Paulik,Bessenyey-Paulik,Walther-Paulik
, p. 75 - 82 (2004)
It is already a generally accepted opini...
Ammonia Absorption on Alkaline Earth Halides as Ammonia Separation and Storage Procedure
Liu, Chun Yi,Aika, Ken-Ichi
, p. 123 - 131 (2007/10/03)
For the low pressure ammonia synthesis (...
7789-41-5 Process route
-
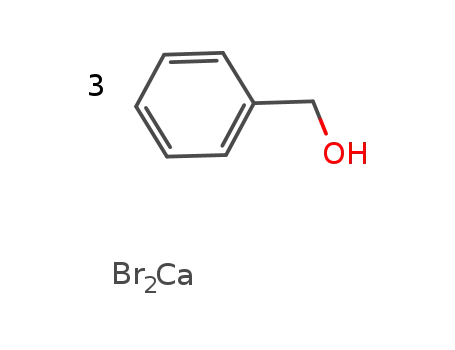
-
calcium bromide * 3 benzyl alcohol

-

- 7789-41-5
calcium bromide
-
- 100-51-6,185532-71-2
benzyl alcohol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In not given; decomposition at touching the satd. solution at 32°C in its components;;
|
-
- 7726-95-6
bromine

-
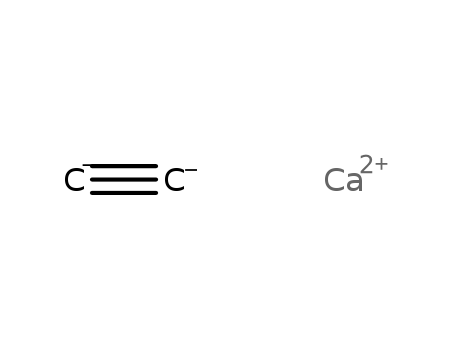
- 75-20-7
calcium carbide

-

- 7789-41-5
calcium bromide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In neat (no solvent); passing of a mixture of Br2 and air over CaC2 forms CaBr2 at heating;;
|
|
|
In neat (no solvent); byproducts: C2Br6; powdered CaC2 (63%) and dry Br2 in closed tube, 5 month at ambient temperature;;
|
>99 |
|
In neat (no solvent); byproducts: C2Br6; touchment of powdered CaC2 and liquid Br2 for some months at normal temperature under formation of CaBr2 and C2Br6;; not isolated;;
|
|
|
In neat (no solvent); byproducts: C; formation of CaBr2 and C in a closed tube at 100°C;;
|
|
|
In neat (no solvent); byproducts: C; longer heating on boiling water bath;;
|
|
|
In neat (no solvent); passing of a mixture of Br2 and air over CaC2 forms no CaBr2 in coldness;;
|
0% |
|
In neat (no solvent); passing of a mixture of Br2 and air over CaC2 forms CaBr2 at heating;;
|
|
|
In neat (no solvent); byproducts: C2Br6; touchment of powdered CaC2 and liquid Br2 for some months at normal temperature under formation of CaBr2 and C2Br6;; not isolated;;
|
|
|
In neat (no solvent); byproducts: C; formation of CaBr2 and C in a closed tube at 100°C;;
|
|
|
In neat (no solvent); passing of a mixture of Br2 and air over CaC2 forms no CaBr2 in coldness;;
|
0% |
|
In neat (no solvent); reaction at 350°C;;
|
7789-41-5 Upstream products
-
7726-95-6
bromine
-
7440-70-2

calcium
-
64-18-6
formic acid
-
781577-54-6
calcium(II) oxalate
7789-41-5 Downstream products
-
188069-06-9
(+/-)-4-Bromo-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)tetrahydrofuran
-
7558-02-3

potassium bromide
-
7647-15-6

sodium bromide
-
7550-35-8

lithium bromide
Relevant Products
-
Barium carbonate
CAS:513-77-9
-
1,4-Butanediol vinyl ether
CAS:17832-28-9
-
Tetraacetylethylenediamine
CAS:10543-57-4